Three Free PHP Accelerator:APC、eAccelerator、XCache Comparison
I have been looking for articles on PHP acceleration,Chance to seeKill offThis article,Feeling good,For everyone to share,Again thank kill off。
one、PHP Accelerator Introduction
PHP is an accelerator in order to improve the efficiency of PHP,Thus from PHP opcode cache,PHP execution behind this would not resolve the converted,PHP opcode can invoke direct,On such speed is increased a lot。
Apache's request to use mod_php、In response to the flow of execution:
1、Apache receives a request。
2、Apache pass the request to the mod_php。
3、mod_php locate a disk file,And loaded into memory。
4、mod_php compile the source code tree becomes opcode。
5、mod_php execution opcode tree。
PHP is the fourth step of the corresponding accelerator,Its purpose is to prevent repeated every request to compile PHP PHP code,Because in high-traffic sites,Often not a lot of compiler execution speed fast? So there are a bottleneck that compiles PHP affects both the speed and load server load,In order to solve this problem,PHP accelerator was born。
two、PHP Accelerator Installation and Configuration
1、APC Installation and Configuration
APC stands for Alternative PHP Cache,The official translation is called "Optional PHP cache",It is an extension of PHP PECL,It seems to be using facebook,Here begin the installation (ubuntu environment):
$wget http://pecl.php.net/get/APC-3.0.19.tgz
$tar xvzf APC-3.0.19.tgz
$cd APC-3.0.19/APC-3.0.19
$/usr/local/php/bin/phpize
$./configure –enable-apc –enable-apc-mmap –with-php-config=/usr/local/php/bin/php-config
$make
$sudo make install
Here we configure APC,Because I changed the path of PECL extension,So I have to move under the compiled file:
$sudo mv /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20060613/apc.so /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/PECL
Then we edit the php.ini configuration file,Please add the following code to the php.ini to:
extension_dir = “/usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/PECL”
extension = apc.so
; APC
apc.enabled = 1
apc.shm_segments = 1
apc.shm_size = 64
apc.optimization = 1
apc.num_files_hint = 0
apc.ttl = 0
apc.gc_ttl = 3600
apc.cache_by_default = on
This will restart apache in phpinfo()Information display。
2、Installation configuration eAccelerator
eAccelerator is actually the predecessor of truck-mmcache,Because the development truk-mmcache Zend people were given amnesty,Therefore, the development eAccelerator who inherited some of the characteristics truk-mmcache,EAccelerator accelerator design。Installation is as follows:
$wget http://jaist.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/eaccelerator/eaccelerator-0.9.5.tar.bz2
$tar -jxf eaccelerator-0.9.5.tar.bz2
$cd eaccelerator-0.9.5
$/usr/local/php/bin/phpize
$./configure –enable-eaccelerator=shared –with-php-config=/usr/local/php/bin/php-config
$make
$sudo make install
$sudo mv /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20060613/eaccelerator.so /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/PECL
The following code to your php.ini file
extension = eaccelerator.so
; eAccelerator
eaccelerator.shm_size = “16”
eaccelerator.cache_dir = “/tmp/eaccelerator”
eaccelerator.enable = “1”
eaccelerator.optimizer = “1”
eaccelerator.check_mtime = “1”
eaccelerator.debug = “0”
eaccelerator.filter = “”
eaccelerator.shm_max = “0”
eaccelerator.shm_ttl = “0”
eaccelerator.prune_period = “0”
eaccelerator.shm_only = “0”
eaccelerator.compress = “1”
eaccelerator.compress_level = “9”
Create cache directory,Restart apache
$sudo mkdir /tmp/eaccelerator
$sudo chmod 777 /tmp/eaccelerator
$sudo /usr/local/apache/apachectl restart
At phpinfo()Check whether the installation was successful.
3、Installation and Configuration XCache
XCache own people as something to be developed,I also do little rookie proud,And XCache in terms of speed and performance are doing well。Here quickly let us taste it now!
$wget http://xcache.lighttpd.net/pub/Releases/1.2.2/xcache-1.2.2.tar.gz
$tar xvzf xcache-1.2.2.tar.gz
$cd xcache-1.2.2
$/usr/local/php/bin/phpize
$./configure –enable-xcache –enable-xcache-coverager –with-php-config=/usr/local/php/php-config
$make
$sudo make install
$sudo mv /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20060613/xcache.so /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/PECL
In php.ini add configuration information:
extension = xcache.so
; xcache
xcache.admin.user = “admin”
xcache.admin.pass = “(carried out) echo ’(Your password)’|md5sum(Resulting ciphertext)”
;
xcache.size = 24M
xcache.shm_scheme = “mmap”
xcache.count = 2
xcache.slots = 8k
xcache.ttl = 0
xcache.gc_interval = 0
xcache.var_size = 8M
xcache.var_count = 1
xcache.var_slots = 8k
xcache.var_ttl = 0
xcache.var_maxttl = 0
xcache.var_gc_interval = 300
xcache.test = Off
xcache.readonly_protection = On
xcache.mmap_path = “/tmp/xcache”
xcache.coredump_directory = “”
xcache.cacher = On
xcache.stat = On
xcache.optimizer = Off
;
xcache.coverager = On
xcache.coveragedump_directory = “”
Create cache directory,Restart apache
$sudo mkdir /tmp/xcache
$sudo chmod 777 /tmp/xcache
$sudo /usr/local/apache/bin/apachectl restart
To view the phpinfo()Information now!
three、PHP Accelerator Test
1、test environment
hardware: AMD Athlon 64 X2 Dual Core Processor 4400+ @ 2.2GHz CPU, 2GB memory. 160GB SATA hard drive
software: Linux Ubuntu server Gutsy 7.10, Apache 2.2.4, MySQL 5.0.45 And PHP 5.2.3
Test instructions: ab -c5 -n3000 http://example.com/ (We are using Apache Benchmark (from) tool,5 concurrent connections,3000Request times)
2、Test Results
No accelerator:
Document Path: /
Document Length: 21757 bytes
Concurrency Level: 5
Time taken for tests: 288.255212 seconds
Complete requests: 3000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 66777000 bytes
HTML transferred: 65271000 bytes
Requests per second: 10.41 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 480.425 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 96.085 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 226.23 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.5 0 19
Processing: 181 479 186.0 444 1822
Waiting: 166 461 184.7 427 1708
Total: 181 479 186.0 444 1822
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 444
66% 525
75% 577
80% 619
90% 732
95% 819
98% 946
99% 1012
100% 1822 (longest request)
APC 加速器:
Document Path: /
Document Length: 21757 bytes
Concurrency Level: 5
Time taken for tests: 98.530068 seconds
Complete requests: 3000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 66777000 bytes
HTML transferred: 65271000 bytes
Requests per second: 30.45 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 164.217 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 32.843 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 661.84 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.0 0 2
Processing: 58 163 71.2 155 2452
Waiting: 53 158 69.6 150 2329
Total: 58 163 71.2 155 2452
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 155
66% 178
75% 193
80% 204
90% 235
95% 258
98% 285
99% 302
100% 2452 (longest request)
eAccelerator加速器:
Document Path: /
Document Length: 21757 bytes
Concurrency Level: 5
Time taken for tests: 95.983986 seconds
Complete requests: 3000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 66777000 bytes
HTML transferred: 65271000 bytes
Requests per second: 31.26 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 159.973 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 31.995 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 679.39 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.1 0 3
Processing: 57 159 91.3 148 3830
Waiting: 50 152 89.8 142 3704
Total: 57 159 91.3 148 3830
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 148
66% 174
75% 193
80% 205
90% 239
95% 263
98% 289
99% 309
100% 3830 (longest request)
XCache加速器:
Document Path: /
Document Length: 21757 bytes
Concurrency Level: 5
Time taken for tests: 99.76300 seconds
Complete requests: 3000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 66777000 bytes
HTML transferred: 65271000 bytes
Requests per second: 30.28 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 165.127 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 33.025 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 658.19 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 0 0.0 0 2
Processing: 59 164 83.4 155 3367
Waiting: 52 156 66.4 148 1802
Total: 59 164 83.4 155 3367
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 155
66% 178
75% 196
80% 206
90% 237
95% 263
98% 287
99% 305
100% 3367 (longest request)
3、Results Summary
| Request Time(second) | Single request time(millisecond) | The maximum memory footprint(MB) | The minimum memory footprint(MB) | |
| None | 10.41 | 96.08 | 24 | 24 |
| APC | 30.45 | 32.84 | 21 | 21 |
| eAccelerator | 31.26 | 31.99 | 23 | 18 |
| XCache | 30.28 | 33.02 | 29 | 19 |
four、PHP accelerator comparison summary
1、EAccelerator obtained by testing at request time and overall memory footprint area is best。
2、Test results using the ratio of the accelerator by accelerator-free request time about three times faster。
3、By observing the various official,XCache is the fastest updates,It also shows that most of the development。
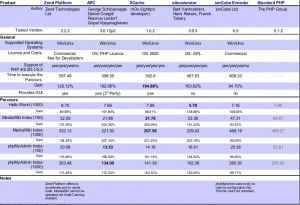
These are the summary results,You might ask me in the end with the accelerator good? I can only tell you,First of all,Use must be better than no,Secondly, each of the accelerator some parameters can tune,So according to your system environment,then,Personally, I think you can study in detail under eAccelerator and XCache,Both still great potential,Finally, I get a map from the results of a more professional test site: